ckd referral guidelines
Cardiovascular disease adverse drug reactions acute kidney injury and prolonged hospital admissions 4-10. This guideline covers care and treatment for people with or at risk of chronic kidney disease CKD.
It aims to prevent or delay the progression and reduce the risk of complications and cardiovascular disease.

. This guide is currently under revision. O Family history of structural renal disease eg cystic kidney disease Staging of CKD Risk staging of kidney disease is important for care planning and patient management. This handbook is a highly regarded evidence-based source of information providing guidance and clinical tips to help you detect manage and refer patients in your practice with CKD.
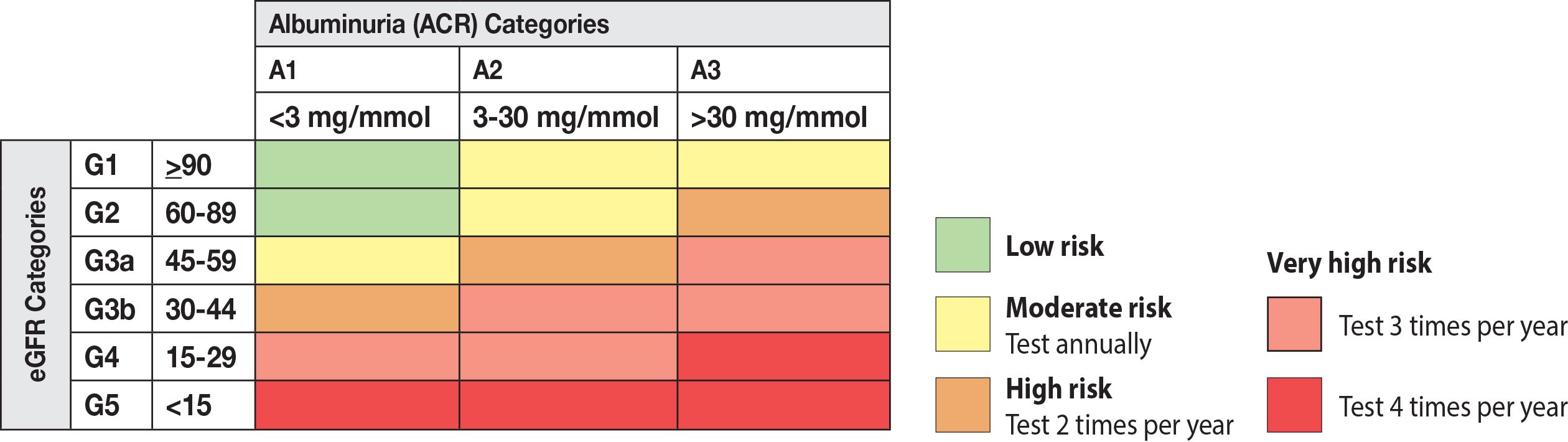
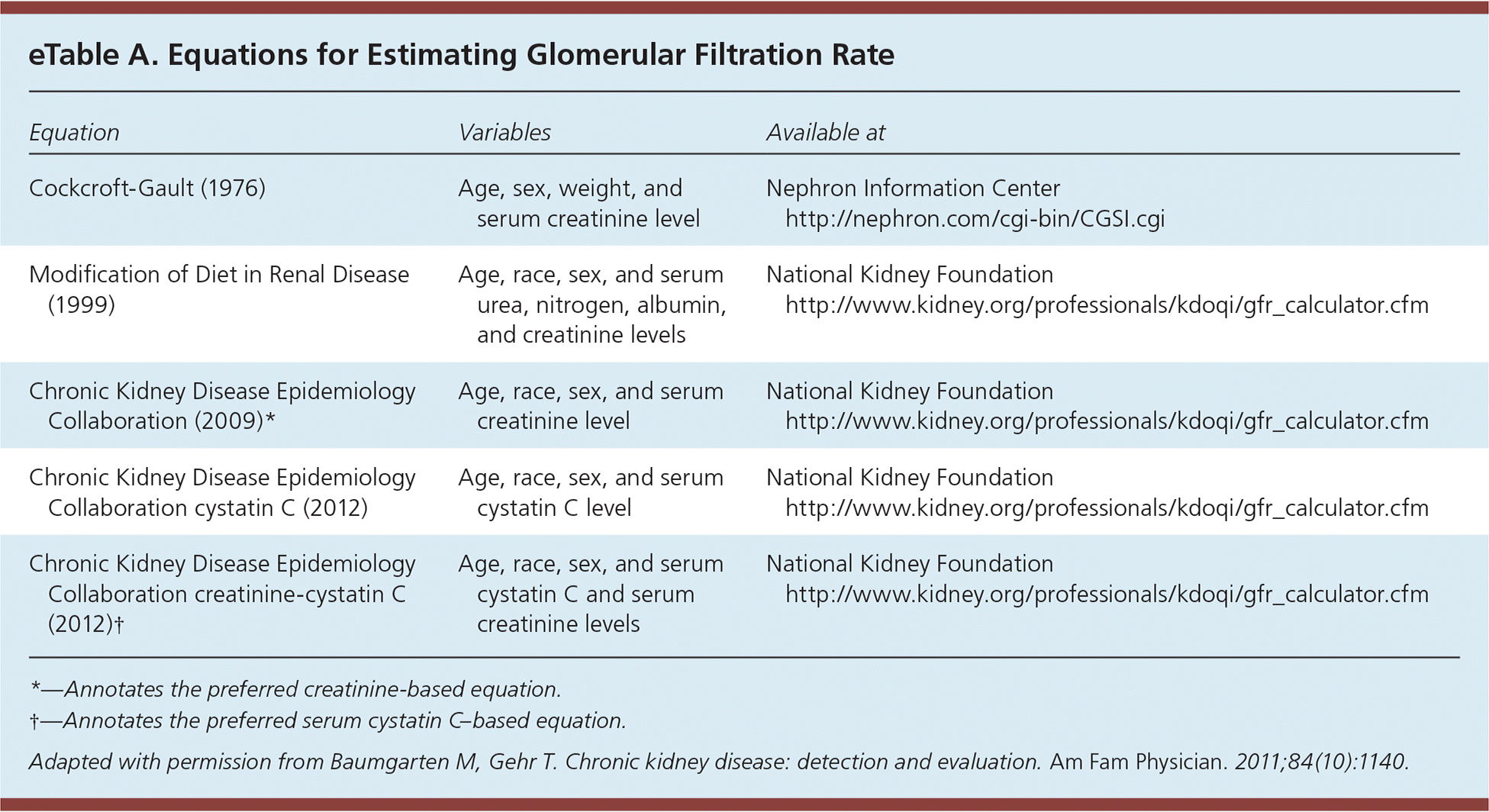
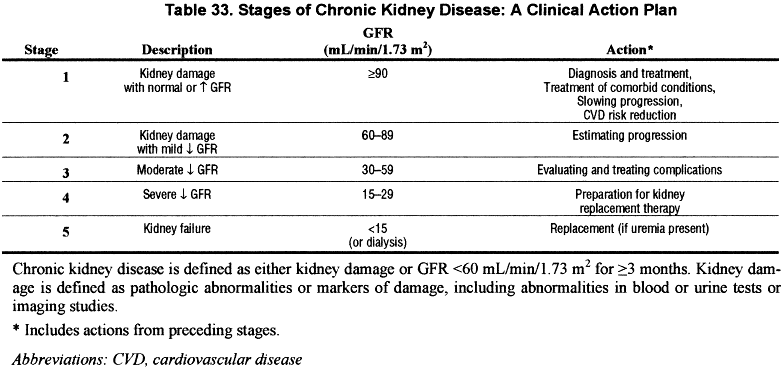
1 90 Normal or increased GFR with other evidence of kidney disease 12 monthly 2 60-89 Slight decrease in GFR with other evidence of kidney disease 12 monthly 3A 45-59 Moderate decrease in GFR with or without other evidence of kidney disease 6 monthly 3B 30-44 Moderate decrease in GFR with or without other evidence of kidney disease 6 monthly. Further details on risk determination are available on the Kidney Disease Improving. EGFR 30 mLmin173m2 irrespective of albuminuria or hematuria.
Markers of kidney damage such as proteinuria urinary albumincreatinine ratio ACR greater than 3 mgmmol urine sediment abnormalities electrolyte and other abnormalities due to. The UK eCKD Guide is derived from the NICE SIGN and the UK Kidney Association guidelines. Kidney care - patient information leaflet.
Colour-coded clinical action plans. But late referrals eGFR. Chronic Kidney Disease guidelines v80 4 November 2021pdf.
The threshold for emergency treatment varies but most guidelines recommend that emergency treatment should be given if the serum K is 65 mmolL with or without ECG changes. Stage eGFR mL per minute per 173 m 2. Frequency of monitoring.
Role of primary and secondary care. Easy to use and interactive the handbook features. Read More Information On A Breakthrough CKD Therapy At The Patient Site.
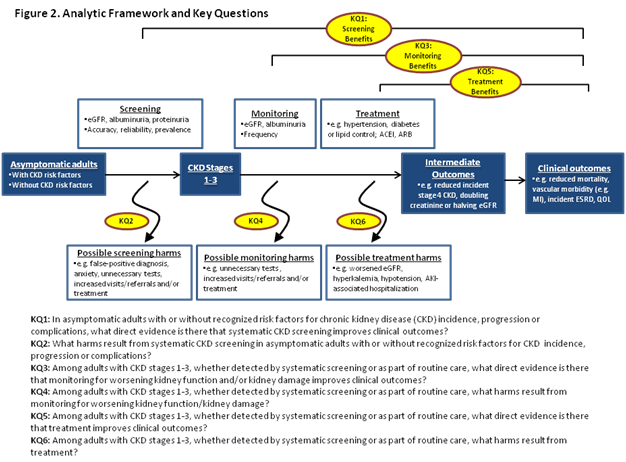
A total of 486 new GP referrals were received in 2012 and 574 in 2016 18 increase post NICE CKD guideline. It also covers managing anaemia and hyperphosphataemia associated with CKD. Chronic kidney disease CKD is a major public health concern that affects approximately 47 million persons in the United States or 148 of the US.
Doing so may reduce the misclassification of CKD in up to 40 of patients and may result in a higher classification stage for 25 of those with CKD. Potassium lowering information sheet - Doctor- Nurse Aug 19 A4pdf. Investigations for chronic kidney disease.
Complications CVD CKD progression other complications. Through the use of guidelines timely referral and a multidisciplinary approach to care the ability to provide effective and efficient care for CKD patients can be improved. Monitor renal function by checking serum creatinine and estimated.
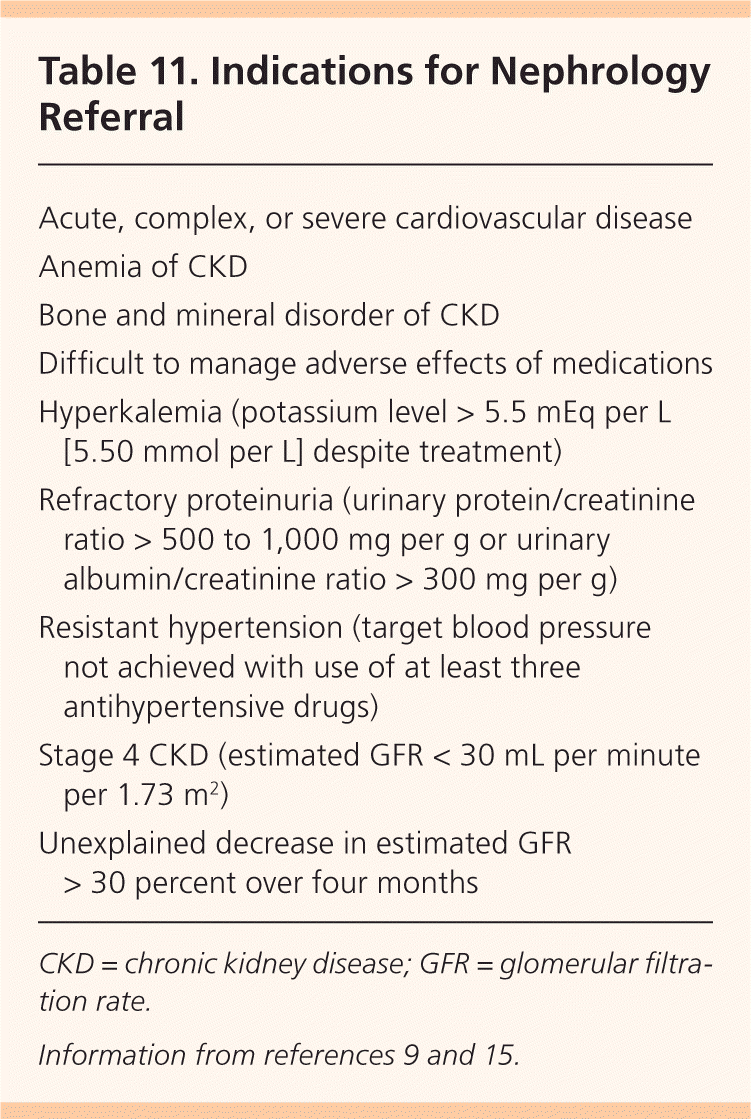
It aims to provide quick online support for the diagnosis and management of CKD. This Guidelines summary covers key recommendations for primary care on the assessment of chronic kidney disease CKD. Stable stage 3 or 4 CKD with no other indication for referral.
Immediate referral - malignant hypertension Routine referral - uncontrolled 15090 BP despite 4 agents at therapeutic doses in a patient with CKD Further info about hypertension in CKD. This guideline is published by the Stroke Foundation. Post NICE fewer stage 4 and 5 CKD patients were being referred.
Imperial renal medication sick-day-rulespdf. An unexplained progressive decline in eGFR 5 mLmin173m2 that occurs over 6 months confirmed on repeat testing within 2-4 weeks ACEi or ARBs can cause a. Ad Chronic Kidney Disease CKD Can Impact Your Gout Treatment Options.
More patients had cholesterol-levels checked. This guideline is endorsed by the RACGP. It aims to prevent or delay the progression and reduce the risk of complications and cardiovascular disease.
Jungers P Massy Z Nguyen-Khoa T et al. Identify any underlying causes and risk factors for disease progression which will influence the frequency of monitoring. Chronic kidney disease.
Overview Background History classification and controversies. CKD is associated with other common chronic diseases such as diabetes hypertension and cardiovascular disease CVD 1 and an estimated 110 British Columbians has some form of significant kidney disease 2. Last formal revision - August 2017.
It also covers managing anaemia and hyperphosphataemia associated with CKD. Donate to the RACGP Foundation today and influence the future of general practice. 800 am to 800 pm AEDT.
Classification of CKD in adults. Learn About a Kidney Safe Treatment That Can Effectively Lower Your Uric Acid Level. Chronic kidney disease CKD is a reduction in kidney function or structural damage or both present for more than 3 months with associated health implications.
Chronic Kidney Disease Management in Primary Care. Persistent albuminuria ACR 60 mgmmol irrespective of hematuria 2-3 samples over 2-4 weeks. NICE has produced a COVID-19 rapid guideline on.
Refer to Figure 1 page 1. Evidence-based guidelines from groups including Renal Physicians Association and NKF provide tools for management of CKD patients by both generalists and nephrologists. BP control had improved.
Referral guidelines Who to screen and when to refer. This guideline covers care and treatment for people with or at risk of chronic kidney disease CKD. Timing of referral of chronic kidney disease patients to nephrology services adult.
If a person has a confirmed diagnosis of chronic kidney disease CKD arrange monitoring for disease progression and associated complications and arrange specialist referral if appropriate. CKD Management Management of CKD. UKKA statement following the 2021 NICE CKD Guideline update Rationale recommendations for.
A quick reference guide. Suspicion of renal involvement from a systemic illness eg myeloma vasculitis sarcoidosis should lead to urgent referral or discussion. The primarysecondary care interface Daniel Ford Consultant Renal Physician UHCW.
The CARI Guidelines. Ad Learn How This Treatment May Help Reduce The Risk Of CKD Progression Dialysis. CKD markedly increases the risk of.
Risk is determined based on Cause eGFR and uACR or CGA. Longer duration of predialysis nephrological care is associated with improved long-term survival of dialysis patients. It aims to prevent or delay progression and reduce the risks of cardiovascular disease.
Chronic Kidney Disease Identification Evaluation And Management Of Adult Patients Province Of British Columbia
Chronic Kidney Disease Detection And Evaluation

Key Guidance From Kdigo 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline For Bp Download Scientific Diagram

Balancing Nephrology Referrals With Nephrologist Capacity To Decrease Emergency Dialysis Starts Kidney International Reports

Practical Approach To Detection And Management Of Chronic Kidney Disease For The Primary Care Clinician The American Journal Of Medicine
Chronic Kidney Disease Detection And Evaluation
Screening For And Management Of Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 1 3 Effective Health Care Ehc Program

Approach To The Detection And Management Of Chronic Kidney Disease The College Of Family Physicians Of Canada
Quick Reference Guide On Kidney Disease Screening National Kidney Foundation
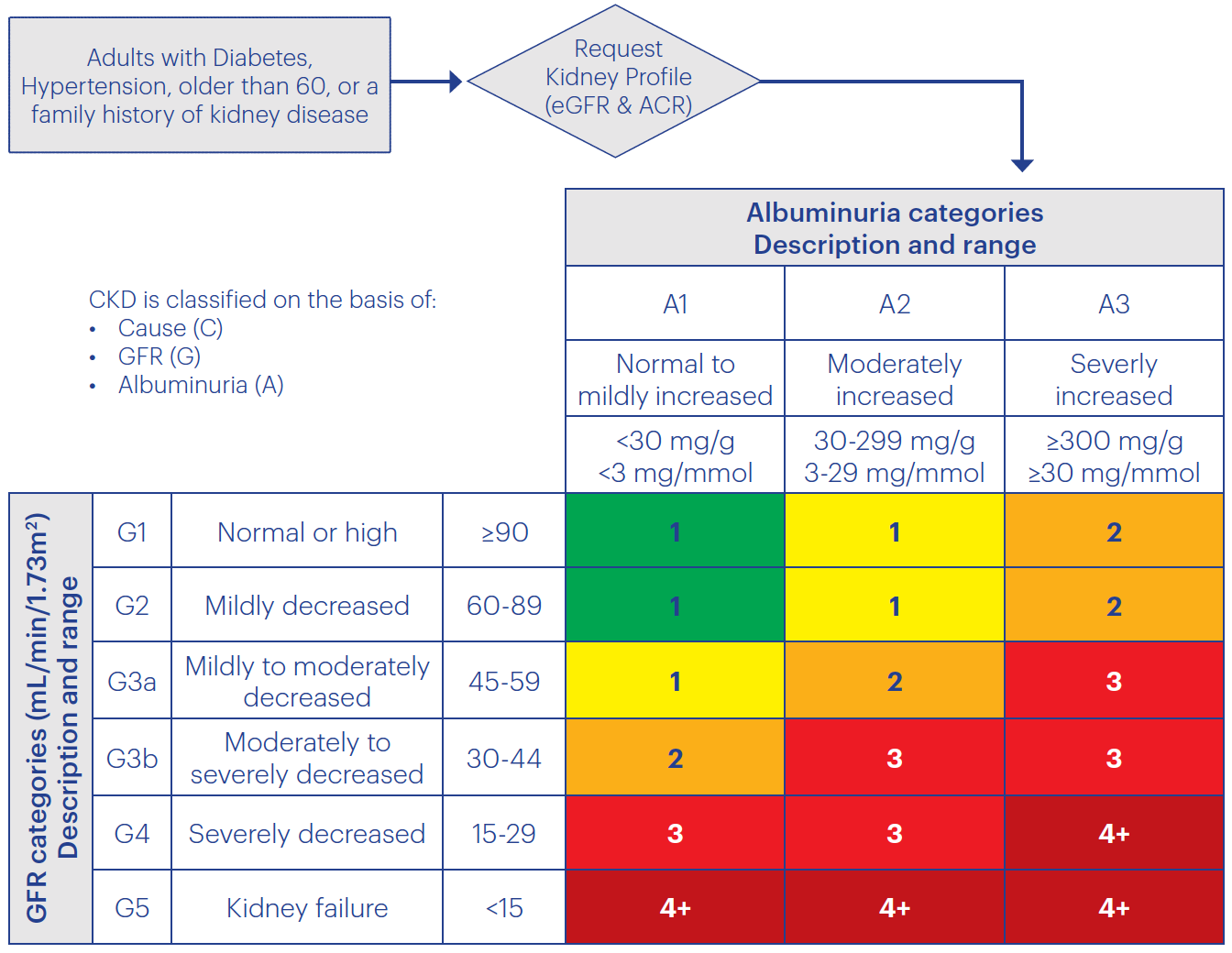
Chronic Kidney Disease Change Package National Kidney Foundation
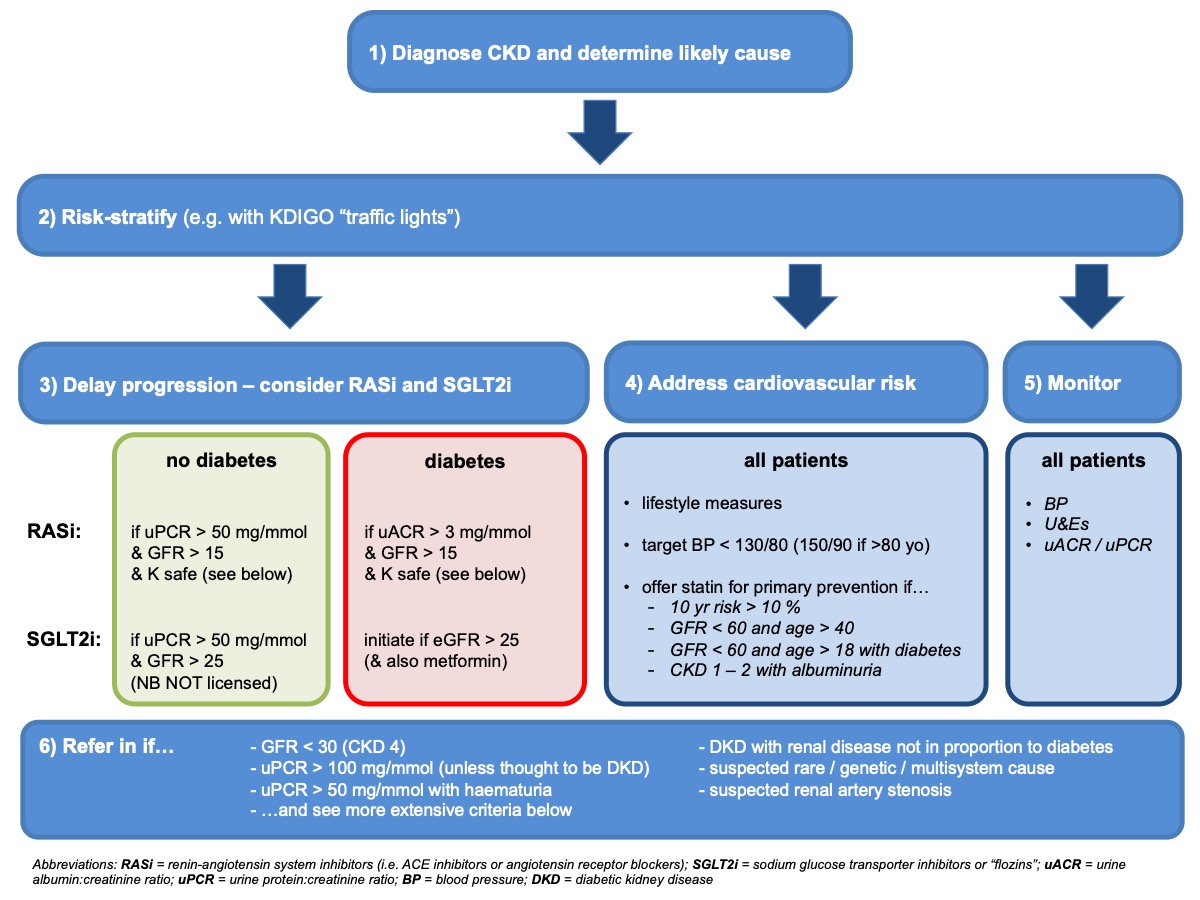
Ckd Summary Overview Edren Org

Chronic Kidney Disease Detection And Evaluation
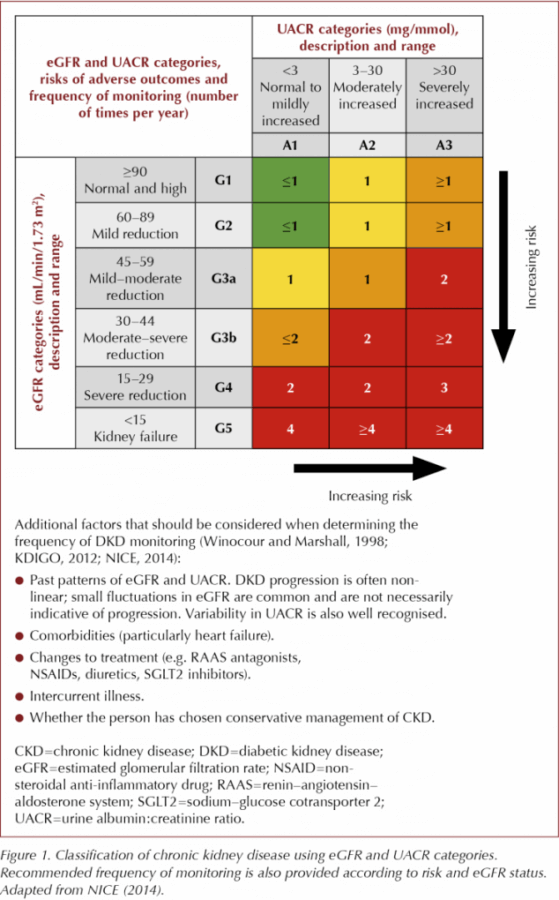
Testing For Kidney Disease In Type 2 Diabetes Consensus Statement And Recommendations Diabetesonthenet

The Summary Of Chronic Kidney Disease Management Guidelines Download Scientific Diagram

Nice Ckd Guideline Nice Guideline Guidelines
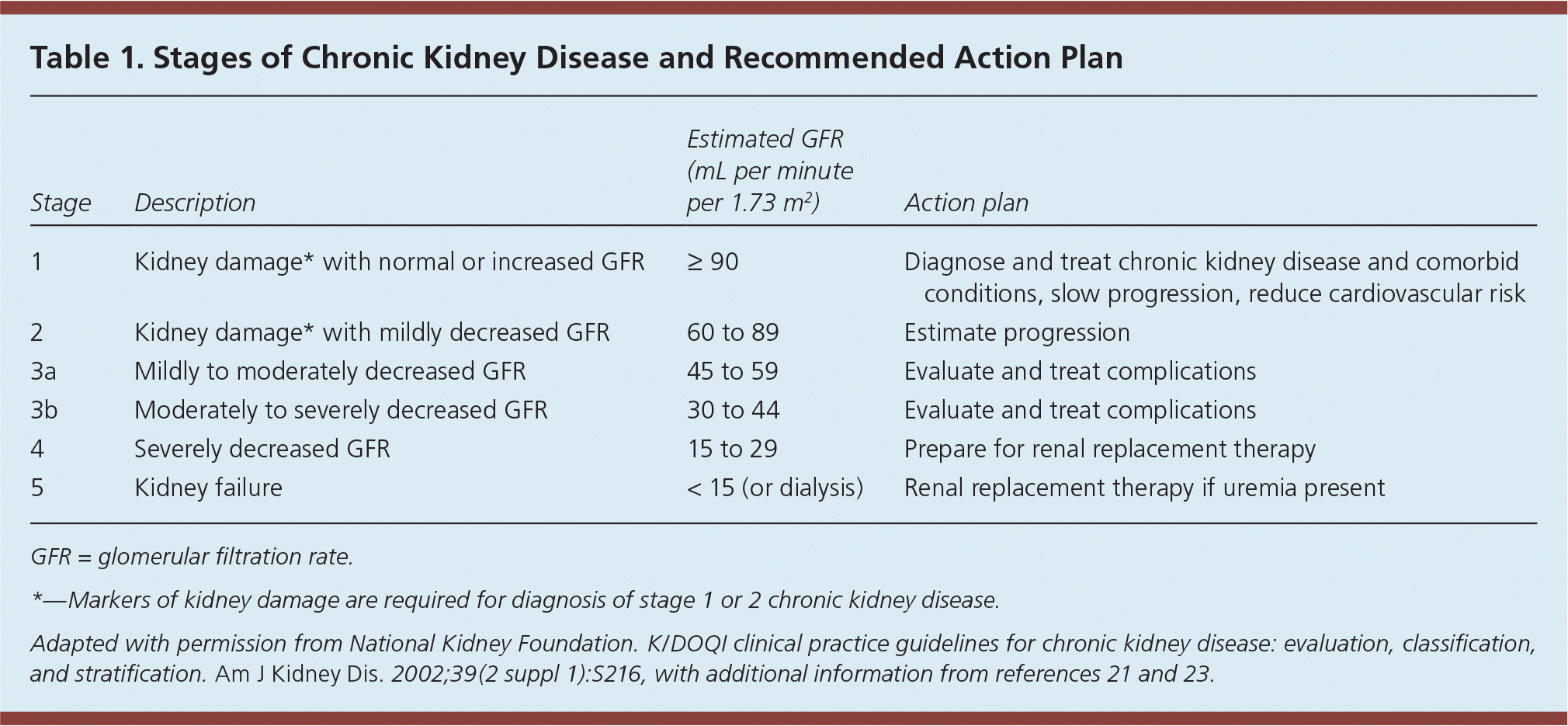
Chronic Kidney Disease Detection And Evaluation

Kidney Function Preservation Pathway Ucla Kidney Health Program Los Angeles Ca

Risk Of Ckd Progression Frequency Of Visits And Referral To Nephrology Download Scientific Diagram
Comments
Post a Comment